- Home
- >
- The Court System
- >
- Structure of the Illinois Courts
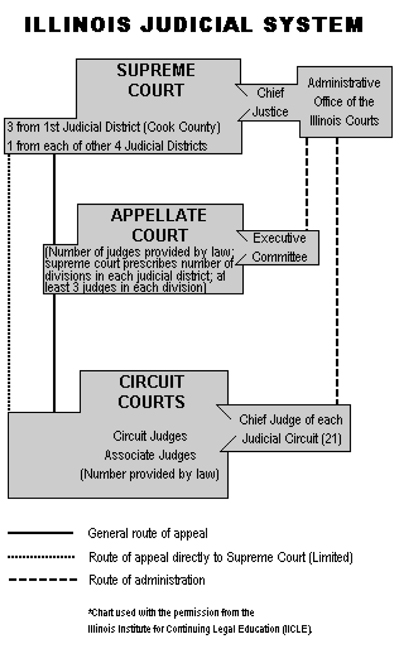
The Supreme Court:
The Supreme Court, highest tribunal in Illinois has seven justices elected from their respective judicial districts for a term of ten years. Three justices are elected from the First District (Cook County), and one from each of the other four districts. The Supreme Court has general administrative and supervisory authority over all courts in the state. This authority is exercised by the chief justice with the assistance of the administrative director and staff appointed by the Supreme Court. The Supreme Court hears appeals from lower courts and may exercise original jurisdiction in cases relating to revenue, mandamus, prohibition or habeas corpus.
The Appellate Court:
The Appellate Court hears appeals from the circuit courts. There are five districts of the Appellate Court, and judges are elected for ten year terms. Cook County, which comprises the First District, has 18 elected appellate judges. The remaining 101 downstate counties are divided into four districts; the third District and the fourth District each elect four appellate judges. The second and fifth District each elect six judges. Additional judges are assigned by the Supreme Court to the Appellate Court, temporarily, on a showing of need. Elgin is the seat of the second District; Ottawa, the third; Springfield, the fourth and Mount Vernon, the fifth.
The Circuit Court:
The unified trial court in Illinois is the circuit court comprised of circuit and associate judges. The state is divided into 23 judicial circuits, each having one chief judge elected by the circuit judges. The chief judge has general administrative authority in his or her circuit, subject to the overall administrative authority of the Supreme Court. Circuit judges may hear any case assigned to them by the chief judge. Associate judges may not preside over criminal cases in which the defendant is charged with an offense punishable by imprisonment for one year or more (felonies), unless approval is received from the Supreme Court. The circuit judges are elected for a term of six years; associate judges are appointed by the circuit judges in accordance with Supreme Court rules for a four year term.
Judicial Appointment, Election and Dismissal:
Although the Fourth Judicial Circuit is a unified circuit with one Chief Judge, all nine counties of the circuit have separate courthouses. Notwithstanding this fact, each of the judges of the Fourth Judicial Circuit may hear cases in each of these counties and be assigned by the Supreme Court to hear cases in any other county within the State.
The Circuit Court is part of the judicial branch of government. Financing is provided from three sources: (1) state funds which finance salaries and benefits of judges and court reporters; (2) state funds which provide reimbursement to the counties to offset the costs of several positions in Court Services (Probation); and (3) county revenues. In order to maintain a productive organization, the judges and their staff work closely with the County Boards in the areas of automation, personnel management, budgeting, purchasing and building maintenance.
When a Supreme, Appellate or Circuit Court judgeship is vacated or newly created, candidates are nominated at primary elections and elected at the general election. However, any judge previously elected may, at the expiration of his or her term, have his or her name submitted to the voters on a special judicial ballot without party designation and without an opposing candidate, on the sole question of whether he or she shall be retained in office for another term.
The Illinois Courts Commission, composed of one Supreme Court judge, two Appellate Court judges and two Circuit judges, has the authority after notice and public hearing, (1) to remove from office, suspend without pay, censure or reprimand any member of the judiciary for willful misconduct in office, persistent failure to perform his duties, or other conduct that is prejudicial to the administration of justice or that brings judicial office into disrepute, or (2) to suspend with or without pay or retire any member of the judiciary who is physically or mentally unable to perform his or her duties.
A Judicial Inquiry Board created by the 1970 Constitution has the authority to conduct investigations, receive or initiate complaints concerning any member of the judiciary and file complaints with the Courts Commission.
Judges and Associate Judges must devote full time to their judicial duties. They may not practice law, hold a position of profit, hold any other office under the United States, this state, unit of local government, or a school district, or hold office in any political party.
DISCLAIMER: The Fourth Judicial Circuit, Office of the Chief Judge provides this web site only as a source of public information on the Fourth Judicial Circuit. All efforts are made to ensure that information and links are accurate and current. However, users should not cite this information as an official or authoritative source and are advised to independently verify all information. Information contained on this web site should in no way be construed as legal advice. Users should contact an attorney if they require legal assistance or advice .
© 2020 Fourth Judicial Circuit Court of Illinois. All rights reserved.
Website by Imagine This! Marketing Group
